In your Linux life time, you may have faced many boot issues. Like you experimented with some stuff and later you found out that you can’t boot into your precious Linux operating system at all!some times installing windows after Ubuntu on same hard disk ...etc
As example ,If you install Windows operating system after you’ve installed a Linux distribution such as Ubuntu, you won’t be able to boot into your Linux operating system. Boot Repair can help.
Anything can go wrong while multi-booting Linux operating systems. Boot Repair can help as well.
Installing Boot Repair:
Try repairing the GRUB bootloader with Boot Repair. Boot to an Ubuntu live session from the live USB/DVD that you used to install Ubuntu. While running an Ubuntu live session open the terminal and type:
Try Ubuntu without installing
from the GRUB menu as shown in the screenshot below
From an Ubuntu live session open the terminal and type:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-repair $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install -y boot-repair $ sudo boot-repair
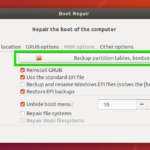
Open the Boot Repair application and select Advanced Options -> Main Options tab -> check Reinstall GRUB and Unhide boot menu as shown in the below screenshot. Click the Apply button. Then reboot the computer with sudo reboot

After reboot , you’ll see GRUB boot menu and boot to your Ubuntu and login .
now if you want to add windows OS to your GRUB menu , open terminal and run thissudo update-grub && sudo reboot
you can also try Boot-Repair-Disk, and runs automatically Boot-Repair rescue tool at start-up
you can download it here
If the OSs were installed in different modes, dual booting Windows and Ubuntu with grub can’t work. If your Windows is installed in BIOS mode, it is recommended to install your Ubuntu in BIOS mode, but if it’s installed in UEFI mode, then do the same with Ubuntu. To check if your Windows is installed in UEFI, press the keyboard combination Windows + r then enter the command msinfo32 in the Run window. In the new window that opens up look for the entry after where it says BIOS Mode.
If you have installed Ubuntu in legacy mode on the same drive with GPT partitioning, you can use Boot Repair’s Advanced options to uninstall grub-pc and install grub-efi-amd64. That converts the Ubuntu installation from BIOS boot to UEFI boot, the same firmware as most recently manufactured laptops with Windows pre-installed have.
Converting Ubuntu into UEFI mode
- Start Boot-Repair, and select Advanced options -> GRUB location tab.
- If you do not see a Separate /boot/efi partition option, this means that your PC does not have any UEFI partition.
- If you see a Separate /boot/efi partition option, put a checkmark in the checkbox to the left of it, then click the Apply button in the lower right corner.

- Set up your BIOS so that it boots the hard drive in UEFI mode. The way to adjust this setting depends on the specific model of the computer, but generally this setting is located in the boot priority settings under the Boot tab of the BIOS/UEFI setup utility.
Converting Ubuntu into BIOS mode
Note: Use this procedure only to convert an UEFI mode Ubuntu installation to boot in BIOS/CSM/legacy mode. Such a conversion may be necessary if some hardware doesn’t work correctly under UEFI mode. (Graphics cards are a common source of problems.) Converting to boot in BIOS/CSM/legacy mode while Windows boots in UEFI mode can make the boot process more awkward — you’ll need to use the computer’s built-in boot manager to switch between OSs, and some computer’s have such poor boot managers that this may be impossible.
- If Ubuntu is installed on a GPT disk (you can check it via the
sudo parted -lcommand), use GParted partition editor to create a BIOS-Boot partition (1MB, unformatted filesystem, bios_grub flag) at the start of its disk. - Start Boot-Repair, and select Advanced options -> GRUB location tab.
- Uncheck the Separate /boot/efi partition option

- Click the Apply button in the lower right corner.
- Set up your BIOS so that it boots the HDD in Legacy mode. Generally this setting is located in the Boot tab → Boot order section of the BIOS.
Converting Windows into GPT mode
MBR2GPT.exe is a command line tool which is located in the System32 folder in Windows 10. With it you can effectively and non-destructively convert a Windows 10 OS disk from MBR (for Legacy BIOS) to GPT partition style (for UEFI) without modifying/deleting any data on the disk or making a clean installation of Windows 10.
source:
https://linuxhint.com/ubuntu_boot_repair_tutorial/








boot-repairv didn’t work for me removed the v and it installed